Category «Pliosauroidea»
Thalassiodracon

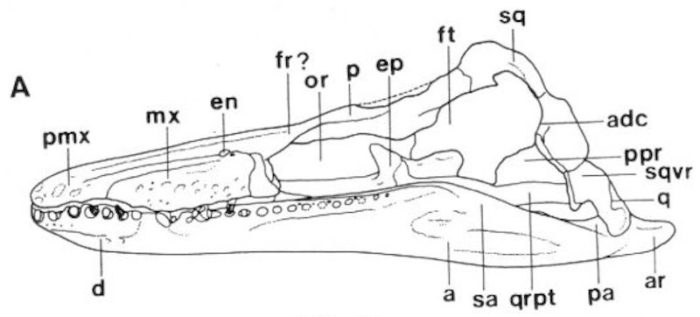
The species Plesiosaurus hawkinsii was introduced in 1838 for a small plesiosaurian from Street, Somerset. The new genus name Thalassiodracon was erected decades later following an examination of a referred skull in Cambridge (CAMSM J.46986). Thalassiodracon means ‘Sea Dragon’, which “alludes to the colloquial description given to the Street marine reptile fauna by Hawkins” (Storrs and Taylor 1996, p.404).
Simolestes

Simolestes has variously been allied with the Pliosauridae and the Rhomaleosauridae. The most noticeable difference between Simolestes and the other pliosaur taxa from the Oxford Clay (Liopleurodon, Peloneustes, Pachycostasaurus), is its much shorter snout and mandibular symphysis, a character is shares with the Rhomaleosauridae.
Rhomaleosaurus
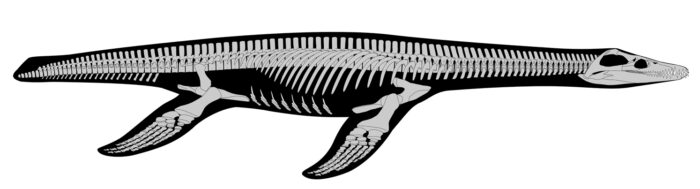
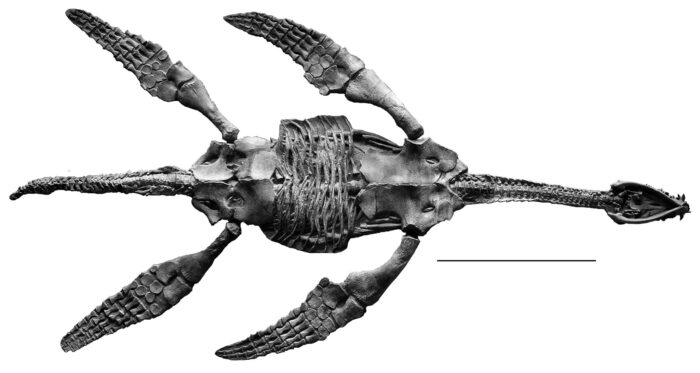
Rhomaleosaurus is the largest known Lower Jurassic pliosaur and was the top predator in early Jurassic marine ecosystems. It has a reinforced skull to help resist torsion and a ferocious set of teeth, a combination of characters perfect for snatching and killing cephalopods, fish, and other marine reptiles.
Peloneustes

Peloneustes is one of several pliosaur genera from the Oxford Clay Formation in the UK. It is one of the better known pliosaurs from this horizon, represented by 12 nearly complete skulls and several skeletons. It is also the most abundant pliosaur from the Peterborough Member of the Oxford Clay Formation (Ketchum and Benson 2011b).
Pachycostasaurus

Pachycostasaurus is approximately 3.1 meters long. Its rib cage and vertebrae exhibit thickened bone (Cruickshank et al. 1996) a condition termed pachyostosis. This heavy ossification is unusual in plesiosaurs (another exception may include Kronosaurus), although it is common in basal sauropterygians, especially pachypleurosaurs.